
Xanthan gum is a versatile polysaccharide used in several bulk manufacturing industries, particularly in the production of gluten-free food products. However, xanthan gum does have an important role in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors, particularly in solid dose formulations. Derived from a natural source, like corn, xanthan gum is extracted through a fermentation process involving the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris. This biopolymer is also known for its capabilities as a binder and stabilizer in tableting formulations.
While Xanthan gum serves as a binder and stabilizer in tableting, it is also naturally suited for the controlled and sustained release of tablets. With its many tableting benefits, there is a significant opportunity for manufacturers to introduce this versatile ingredient as an excipient to their product formulations. It is worth examining the economic and operational advantages of xanthan gum in solid dose production; it has the potential to generate cost savings, efficiency improvements, and product quality enhancements for manufacturers in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical spaces.
Like mentioned before, xanthan gum can act as a binder and disintegrant in tablet formulations. Its binding properties ensure that tablets are compact and cohesive, facilitating ease in handling and durability in packaging. As a disintegrant, xanthan gum aids in the rapid breakdown of the tablet upon contact with moisture in the gastrointestinal tract, ensuring timely release and absorption of the active ingredients. With these two functions, there is no need to incorporate multiple specialized excipients, simplifying the formulation and production process while cutting down on the cost of purchasing more excipients
When comparing xanthan gum to other tablet binders, here are some advantages to consider:
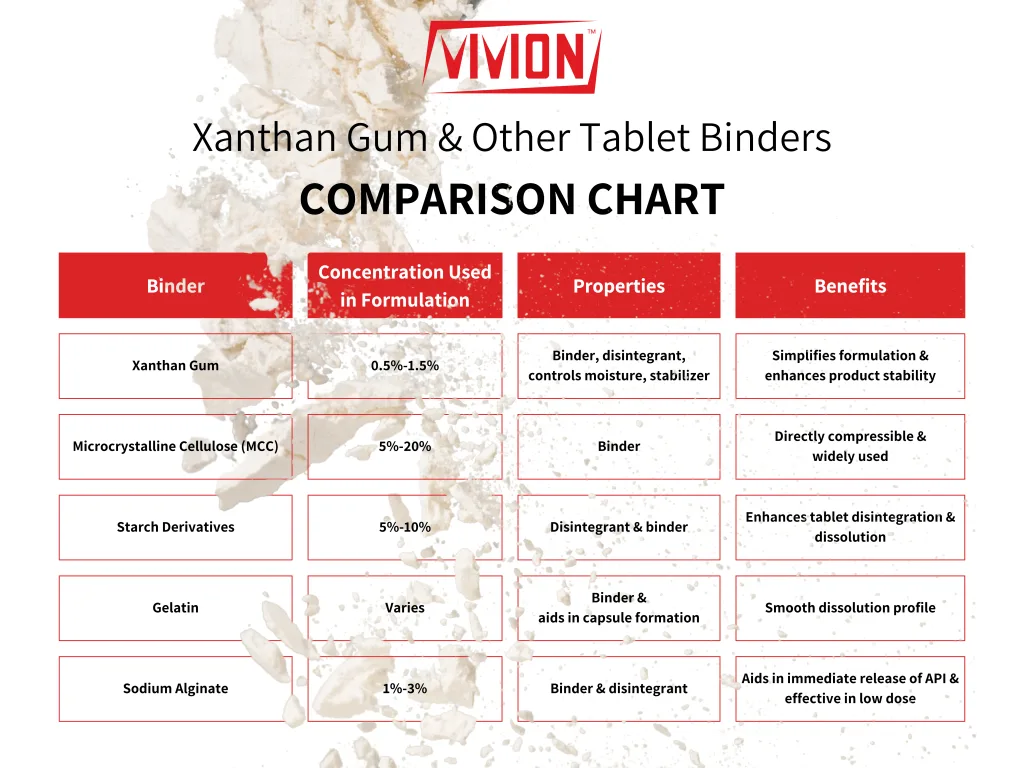
By using xanthan gum in solid dose formulations, manufacturers in both industries can experience cost savings through using fewer excipients, simplified manufacturing processes, and improved product stability and efficacy. This makes xanthan gum a cost-effective solution that does not compromise on quality or consumer appeal.
In the pharmaceutical industry, using xanthan gum not only simplifies the formulation but also has the potential to enhance the manufacturing process. By acting as both a binder and disintegrant, xanthan gum eliminates the need for multiple excipients, so separate sourcing, testing, and validation for each additional excipient is no longer needed. This reduced excipient diversity simplifies inventory management, decreasing the storage requirements and minimizing the risk of supply chain disruptions. Streamlined formulations can also translate into shorter and more efficient production cycles, affecting labor and operational costs.
Xanthan gum’s impact on improved disintegration directly impacts the bioavailability of drugs, potentially allowing for the formulation of tablets with lower doses of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Since APIs often are a significant portion of the production cost, enhancing their efficacy can lead to cost savings. Better bioavailability means that the therapeutic effect can be achieved more reliably, increasing the overall quality and effectiveness of the pharmaceutical product.

Consumer demand for natural and clean-label products has been rising in the nutraceutical sector, with more than 81% of consumers believing it is important to purchase clean-label food products alone. Xanthan gum, derived through natural fermentation processes, meets these consumer preferences by replacing synthetic excipients with a natural alternative. Xanthan gum not only aligns with current market trends but also simplifies the product labels, making them more appealing to health-conscious consumers. Simplified labels are easier for consumers to read and understand and can enhance the perceived value and trustworthiness of the product.
Also, the stabilizing properties of xanthan gum reduce the need for overages—extra amounts of nutrients included in formulations to ensure that the product meets nutritional claims throughout its shelf life. Reducing overages not only cuts down on the direct costs of these added nutrients but also optimizes the manufacturing process by improving the precision and efficiency of production.
By integrating xanthan gum into solid dose formulations, manufacturers in both pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries can enjoy cost savings, which come from the reduced amount of excipients in formulations, enhanced production efficiencies, and improved stability and efficacy of the final products. Additionally, the ability of xanthan gum to meet regulatory requirements and consumer demands for cleaner labels adds to its appeal as a cost-effective formulation ingredient.
Xanthan gum’s role as a strategic component in the development of solid dose products results from these benefits, delivering economic advantages without compromising on quality or market appeal. By adopting xanthan gum, companies could not only streamline their production processes but also position their products more favorably in competitive markets.
As an ingredient, xanthan gum is valued for its ability to enhance the stability and extend the shelf life of solid dose products. A hydrophilic polymer, xanthan gum effectively absorbs and retains moisture, which is crucial in preventing the premature breakdown of tablets in various environmental conditions. This moisture-control property helps maintain the structural integrity and bioavailability of the product throughout its intended shelf life, significantly reducing the degradation of active ingredients over time.

The ability of xanthan gum to stabilize formulations can mean cost savings for manufacturers. By preventing product degradation, the stability that xanthan gum introduces to a formulation can help avoid batch failures (and wasted product) while decreasing the need for costly overages. Improved stability could also result in fewer customer complaints and returns due to faulty products, safeguarding the manufacturer’s brand reputation and circumventing the expenses associated with handling returns and customer service.
With xanthan gum, companies can not only achieve technical and manufacturing excellence but also deliver superior products that meet consumer expectations for quality and value. These advantages make xanthan gum a strategic choice for companies aiming to optimize their production processes and ensure competitiveness in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical market.
Xanthan gum’s contribution to cost-efficiency and improved product quality establishes it as a strategic asset for companies focused on optimizing their tablet manufacturing operations. From its role as an effective binder and disintegrant that reduces the complexity and cost of production processes, to its ability to enhance the stability and extend the shelf life of products, xanthan gum proves to be more than just an excipient. Formulating with xanthan gum ensures operational efficiencies, reduces waste, and minimizes the economic impact of returns by promoting product integrity over time.
Evaluating xanthan gum’s application in your operations and product development can lead to improvements in both cost management and product performance. As the industry continues to evolve, with increasing demands for high-quality, cost-effective, and consumer-friendly products, integrating xanthan gum into your formulations could be a strategic step towards achieving these goals.
See how xanthan gum can revolutionize your pharmaceutical and nutraceutical formulations today by partnering with Vivion, the leading wholesale supplier of high-quality ingredients. With our extensive inventory and industry expertise, Vivion is ready to be your sourcing solution to support your production goals, from cost reduction to enhancing product quality. Contact us to learn more about our products and how we can help boost your manufacturing processes.
https://www.britannica.com/topic/xanthan-gum
https://sphinxsai.com/2014/phvol6pt4/3/(1322-1326)S-2014.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9967536/
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=172.695
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/xanthan-gum